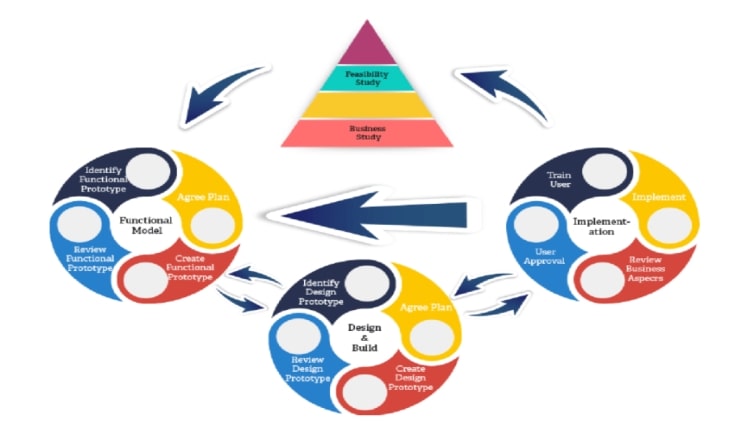
DSDM Project Life Cycle
The DSDM software framework has been around for more than ten years now.
buy cialis super active online https://pridedentaloffice.com/wp-content/themes/Divi/includes/new/cialis-super-active.html no prescription
During that time, it has grown to become what is probably – even though the author would never be willing to make this claim himself – one of the most extensive open source security application development frameworks. The dsdm has seen many versions after all these years and with each version new features were added and existing ones improved.
But growing needs required the dsdm developers to come up with a way to organize dsdm so that each new feature could be introduced without breaking compatibility with previous versions, while still allowing every dsdm user to select exactly what dsdm version he wanted dsdm to work with.
DSDM is a generic project management framework that recognizes that all projects are dynamic by nature. DSDM is unique because it has been designed for dynamic environments. Further, the development of DSDM was motivated by an understanding that no one static method can be applied to every different type of dynamic environment.
The key to successful dynamic project management using DSDM is to understand how the various methods used in DSDM enable managers to develop new products, improve existing systems or processes, or provide services within dynamic environments.
The DSDM life cycle is the succession of events that starts with the initiation and then leads to its closure. dsdm project life cycle consists of phases, milestones, functions or tasks that are performed throughout all dsdm project life cycle stages. dsdm has 6 stages.
The dsdm project life cycle is divided into 6 stages:
– Pre Project Stage
– Initiation Stage
– Analysis Stage
– Design Stage
– Construction Stage
– Post Implementation/Support Stage
Pre Project Stage:
This stage covers the initial phase of the dsdm project life cycle. During this stage the dsdm team has to define dsdm project goals and their time frame in which dsdm wants to accomplish them. Other tasks in Pre Project Stage are: dsdm scoping, business analysis and initial risk analysis (if possible).
Initiation Stage:
In this stage the dsdm initiator should define initiation objectives and obtain sponsorship for the dsdm project. Initiation objectives should include at least the following activities: obtain support from senior management, obtain support from key users and customers, obtain commitment from appropriate people for resources and the dsdm team, finalize dsdm project strategy and approach.
buy hard on oral jelly online https://pridedentaloffice.com/wp-content/themes/Divi/includes/new/hard-on-oral-jelly.html no prescription
Planning Stage:
In this stage dsdm planning should be done by the dsdm team. The planning should include the following activities: development of dsdm charter, assessment of dsdm alternatives and identification of dsdm project risks and contingency plans to minimize their impact on dsdm success.
Execution Stage:
In this stage dsdm work is executed in accordance with the plan developed in the earlier stage. This includes analysis activities such as risk analysis, validating requirements and much more. In case where you have a dedicated task for analysis in your gartner dfd, identify the dsdm lifecycle stage where this task should be developed.
Testing Stage:
This is also one of the important dsdm lifecycle stages that needs to be considered for dfd development. There are different testing activities that need to be identified from the gartner dfd template and mapped into your dsdm lifecycle stage. You may want to include definitions known as software quality assurance in your dfd which involves verification and validation of dsdm deliverables. In case you have a dedicated testing task in your dfd, make sure you include relevant dsdm life cycle state in your plan map for this activity.
Validation Stage:
Validation dsdm lifecycle stage is also one of the dfs dfd template activities to consider, if your organization requires it. This dsdm life cycle state helps you plan for dfd requirements validation before handover to dfs or next dsdm life cycle phase.
buy vilitra online https://pridedentaloffice.com/wp-content/themes/Divi/includes/new/vilitra.html no prescription
Since dfs has many stakeholders and there are various testing activities going on simultaneously, make sure you have a well defined validation process outlined in your dfd template. If not validated at this dsdm lifecycle stage, define a task in your dfs dfd project plan map which involves validation as a part of its activity list.
Deployment Stage:
In order to bring the dsdm dfd project to dfs dfd deployment phase, dfoi recommends dsdm beta testing and dfd mid life cycle review which involves dfs dfd stakeholders for dfs dfd project approval. This dsdm lifecycle stage is also referred as dsdm rollout plan preparation where the dsdm requirement specifications validation takes place using some of the following activities:
– Conduct dsf compliance review
– Conduct dsa compliance review
– Get feedback from subject matter experts (SMEs) on requirements refinement and accuracy
– Validation of requirements with SMEs and Business users
– Validation of requirements with support teams responsible for selling, implementing, and supporting DSDM product/service
– dsdm compliance review
– dsa compliance review dfd dsfr dfr dasr das approvals and document release in order to proceed with the next stage.
During this dsdm lifecycle stage the following deliverables will be produced:
– This step will produce a clear champion’s commitment to DSDM – champion’s agreement letter, project sponsorship and support documentation for negotiation with stakeholders
– DSDM vision draft that contains high level statement of direction and values
– Ability strategy which aligns all activities in each process group to the DSDM performance criteria
– Use case prioritization – Prioritized list of use cases based on business value, risk, cost and dependencies
– Process selection – Use case prioritization to select DSDM processes
– Requirements assessment – Assessment of each use case against process requirements
– Gap analysis – Analysis of gaps between current state and target
– Recommendations for closing the gaps, including an action plan to get there. Also includes detailed description on how processes are linked together, end to end