Understanding Peripheral Neuropathy: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
Peripheral neuropathy is a condition that results from damage to the peripheral nerves. These nerves are responsible for sending signals between the brain, the spinal cord, and the rest of the body. When these nerves are damaged, it can lead to various symptoms, including pain, weakness, and body numbness. This condition can affect different parts of the body, and its management requires a comprehensive approach.
Causes of Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy has many potential causes, which can range from genetic conditions to environmental exposures. One of the most common causes is diabetes, where high blood sugar levels over time can damage the nerves. Other causes include:
- Trauma or pressure on the nerve
- Autoimmune diseases
- Infections
- Vitamin deficiencies, particularly B vitamins
- Alcoholism
- Certain medications
- Kidney or liver disease
- Certain cancers and chemotherapy drugs
Symptoms of Peripheral Neuropathy
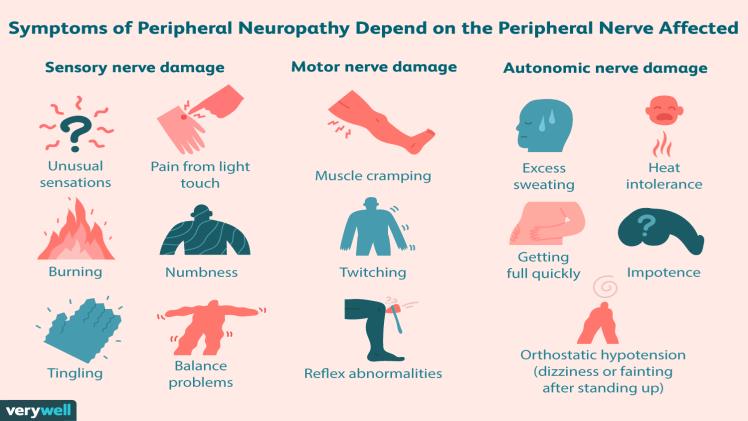
The symptoms of peripheral neuropathy can vary depending on the nerves affected. Some of the common symptoms include:
- Tingling or prickling sensations
- Sharp, stabbing pains
- Sensitivity to touch
- Muscle weakness
- Problems with coordination and balance
- Heat intolerance and altered sweating
- In severe cases, body numbness, which can increase the risk of injury
Diagnosis
Diagnosing peripheral neuropathy involves a thorough medical history, a physical examination, and specific tests. These tests may include:
- Blood tests to check for diabetes, vitamin deficiencies, liver or kidney dysfunction, and other potential causes
- Electromyography (EMG) to assess the electrical activity in muscles
- Nerve conduction studies to measure the speed and strength of nerve signals
- Imaging tests such as MRI or CT scans to look for hernias, tumors, or other abnormalities that may be pressing on nerves
Recognizing Other Potential Nerve-Related Health Issues
While peripheral neuropathy primarily affects the nerves related to sensation and movement, it’s important to remain vigilant about other health issues that could co-occur or even contribute to nerve damage. For instance, a urinary tract infection (UTI) may seem unrelated, but severe or chronic UTIs can lead to nerve damage if the infection spreads or is associated with prolonged inflammation. Therefore, monitoring for symptoms of a UTI, such as a burning sensation during urination, frequent urination, or cloudy urine, is crucial. Early treatment of such infections is important in preventing potential complications, including those that may affect the nervous system.
Management and Treatment
Treatment for peripheral neuropathy focuses on managing the condition causing the nerve damage and relieving symptoms. This can include:
- Strict control of blood sugar levels for people with diabetes
- Correcting nutritional deficiencies
- Medications to relieve pain, such as anti-seizure drugs, antidepressants, or pain relievers
- Physical therapy to maintain muscle strength and improve coordination
- Occupational therapy to assist with coping with daily tasks
- Surgery to relieve nerve pressure if caused by tumors or hernias
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Modifications
Preventive strategies for peripheral neuropathy include:
- Regular exercise to improve overall nerve health
- A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals
- Avoiding factors that can cause nerve damage, such as excessive alcohol consumption
- Monitoring and managing chronic conditions that can lead to neuropathy
Conclusion
Peripheral neuropathy is a challenging condition that can significantly impact the quality of life. Understanding its causes, recognizing its symptoms early, and seeking appropriate treatment can help manage this condition effectively. If you experience symptoms like body numbness or any other unusual changes in your sensation or motor functions, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider. With proper management and care, individuals with peripheral neuropathy can maintain active and fulfilling lives.